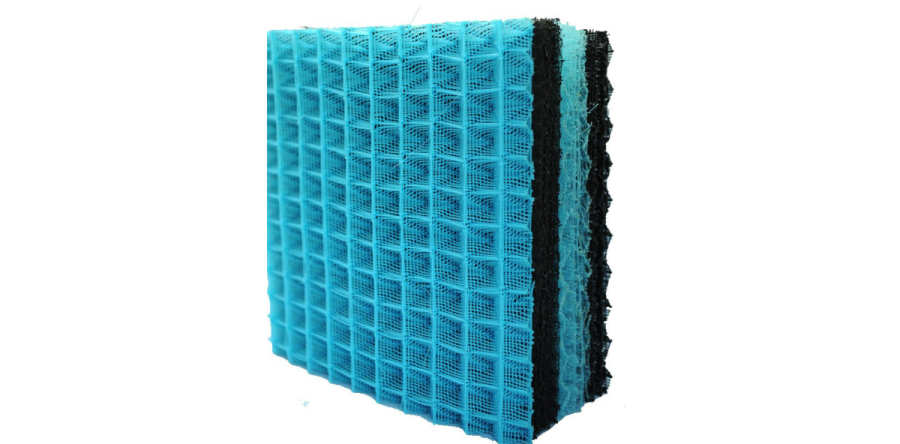
In wet scrubber systems, mist eliminators—also referred to as moisture eliminators or mist eliminator filters—are essential components for achieving efficient gas-liquid separation. Their performance is tightly coupled with system-wide outcomes such as emission control, operational uptime, and protection of downstream assets.
The design of a mist eliminator fundamentally governs its efficiency in capturing entrained droplets, minimizing pressure drop, and resisting fouling under varying process conditions. Kimre’s engineering-driven approach to mist elimination focuses on aligning material science, structural configuration, and system dynamics to ensure optimal performance under real-world industrial conditions.
Critical Engineering Parameters in Mist Eliminator Design
1. Material Selection: Chemical Resistance and Thermal Integrity
The selection of construction materials for a mist eliminator filter must reflect both the chemical environment and mechanical operating parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow regime.
Typical Materials Used:
-
Stainless Steel Alloys (e.g., 316L): High mechanical integrity and corrosion resistance; ideal for high-temperature applications involving oxidizing agents.
-
Engineered Thermoplastics (e.g., PTFE, PVDF, Polypropylene): Preferred in acidic or halogenated gas environments with moderate thermal loads.
-
Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastics (FRP): Lightweight and structurally robust; suitable for scrubbers in fertilizer, battery, or chlor-alkali plants.
Material compatibility must also account for the system’s cleaning procedures (e.g., chemical cleaning, steam injection). Suboptimal material selection may lead to polymer embrittlement, corrosion fatigue, or accelerated fouling—ultimately compromising mist eliminator performance and service life.
2. Mesh and Fiber Bed Configuration: Droplet Removal and Pressure Drop Balance
Mesh-type moisture eliminators and fiber bed assemblies dominate when high-efficiency droplet removal is required, especially in applications involving submicron mist or corrosive aerosols.
Key Design Parameters:
-
Fiber Diameter & Packing Density: Fine fibers and higher packing densities increase droplet interception via diffusion and inertial impaction but also elevate the pressure drop.
-
Layer Configuration: Multilayered mesh pads allow optimization between fine droplet capture and drainage performance. Lower-density outer layers aid in coalesced liquid removal, while denser core layers enhance capture efficiency.
-
Drainage Performance: Efficient liquid removal prevents re-entrainment and minimizes hydraulic loading.
Applications such as sulfuric acid plants, nitric acid absorbers, and phosphoric acid production lines benefit from these designs due to their ability to capture acid mists and protect downstream heat exchangers and process ducting.
3. System Placement and Flow Management: Ensuring Uniform Operation
The positioning of the mist eliminator filter within the scrubber column is critical to maintaining performance stability and separation efficiency.
Optimal Placement Strategy:
-
Located downstream of the gas-liquid contact zone to intercept entrained droplets formed during scrubbing.
-
Allows sufficient residence time for droplet coalescence before separation occurs.
Flow Conditioning:
-
Use of flow straighteners or perforated plates upstream of the mist eliminator helps promote uniform velocity profiles and laminar flow.
-
Prevents channeling, localized overloading, and dry spots, all of which can impair collection efficiency and lead to re-entrainment.
Achieving homogenous gas flow across the mist eliminator surface is essential to maximize surface area utilization and minimize pressure differentials.
Also Read :
The Basics of Mist Eliminators
Understanding The Selection Of Mist Eliminators
Additional Design Practices for Performance Optimization
To ensure long-term functionality and minimal downtime, mist eliminator design should incorporate several auxiliary features:
-
Sloped Drainage Paths and Ports: Enable rapid removal of captured liquid, reducing static loading and potential for corrosion or biofouling.
-
Modular Design Philosophy: Facilitates partial replacements and targeted maintenance without requiring full shutdowns.
-
Maintenance Access Points: Mist eliminators should be designed for easy inspection and cleaning, especially in continuous process environments.
These engineering enhancements improve operational reliability under fluctuating gas loads or high particulate environments.
Industry-Specific Requirements for Mist Eliminators
Performance demands for moisture eliminators vary significantly across industries:
|
Industry
|
Primary Challenges
|
|---|---|
|
Fertilizer Production
|
Aggressive acid gases, particulate loading; requires corrosion-resistant mesh filters
|
|
Petrochemical Plants
|
Fine aerosol separation; balancing pressure drop and maintenance frequency
|
|
Power Generation
|
Long run-time with minimal fouling; focus on mechanical durability
|
|
Metal Processing
|
High solids and acid vapors; risk of erosion and fouling
|
|
Cement & Lime Plants
|
Mist capture to prevent deposition and corrosion in downstream air handling units
|
Kimre’s engineered mist eliminators are tailored to meet each sector’s regulatory, mechanical, and chemical performance targets.
The Risks of Inadequate Mist Eliminator Filter Design
A poorly specified mist eliminator filter can lead to:
-
Increased entrainment of hazardous or corrosive droplets.
-
Accelerated fouling and pressure drop across the scrubber.
-
Corrosion and degradation of downstream components.
-
Non-compliance with emissions regulations and associated penalties.
High-efficiency moisture elimination is critical for meeting environmental standards such as MACT, BREF, and local air quality regulations.
Engineered Solutions from Kimre
With over five decades of field-proven experience, Kimre mist eliminators are purpose-built to meet the challenges of complex gas-liquid systems. Our high-efficiency mesh pad and fiber bed designs are customized using process-specific input data to ensure optimal droplet removal, reduced pressure drop, and maximum service life.
Kimre delivers:
-
Chemically resistant mesh and fiber bed configurations
-
Scalable modular designs for large scrubbers
-
Process-specific modeling and CFD support
-
Global technical support and field services
Optimize Your Scrubber Performance Today
If your wet scrubber system suffers from carryover, fouling, or inconsistent separation efficiency, it may be time to re-evaluate your mist elimination solution.
Contact Kimre to explore tailored mist eliminator designs engineered for your exact process conditions.